



Revision History
|
Rev. |
Description of Modification |
Date |
|
0. |
First issue for comments |
14/7/2022 |
|
1. |
Revised according to IECs comment |
17/8/2022 |
|
2. |
Revised according to IECs comment |
26/8/2022 |
|
3. |
Revised according to IECs comment |
20/9/2022 |
|
4. |
Revised according to IECs comment |
30/9/2022 |
|
5. |
Revised according to IECs comment |
7/10/2022 |
Table of Content
2.2 Monitoring Equipment and Methodology
2.3 Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and Duration
3.2 Water Quality Parameters and Monitoring Frequency
3.4 Monitoring Equipment and Methodology
3.5 Laboratory Measurement and Analysis
4.1 Revision for Inclusion in the EM&A Manual
List of Tables
|
Table A1 |
Summary of Baseline 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results |
|
Table A2 |
Calculated Action and Limit Levels for 1-hour TSP |
|
Table A3 |
Summary of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Results |
|
Table A4 |
Derived Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality |
|
Table 2.1 |
Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Equipment |
|
Table 2.2 |
Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and Duration |
|
Table 2.3 |
Original Air Quality Monitoring Stations for Baseline and Impact Monitoring |
|
Table 2.4 |
Updated Air Quality Monitoring Stations for Baseline and Impact Monitoring |
|
Table 2.5 |
Photo of Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Stations |
|
Table 2.6 |
Summary of Baseline 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results |
|
Table 2.7 |
Action and Limit Levels for Air Quality during Construction Period |
|
Table 2.8 |
Calculated Action and Limit Levels for 1-hour TSP |
|
Table 3.1 |
Parameters measured in the Baseline Water Quality Monitoring |
|
Table 3.2 |
Original Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations |
|
Table 3.3 |
Updated Location of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations |
|
Table 3.4 |
Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Equipment |
|
Table 3.5 |
Detection Limits and Precision for Water Quality Determinates |
|
Table 3.6 |
Analytical Methods Applied to Water Quality Samples |
|
Table 3.7 |
Summary of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Results |
|
Table 3.8 |
Determination of Action and Limit Levels of Water Quality for Impact Monitoring |
|
Table 3.9 |
Derived Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality |
List of Figures
|
Figure 2.1 |
Air Quality Monitoring Locations |
|
Figure 2.2 |
Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Schedule |
|
Figure 3.1 |
Locations of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations |
|
Figure 3.2 |
Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Schedule |
List of Appendices
|
Appendix A |
Air Quality and Water Quality Monitoring Equipment Calibration Certificates |
|
Appendix B |
Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Results and Graphical Presentation |
|
Appendix C |
Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Data and Graphical Presentation |
|
Appendix D |
|
|
Appendix E |
|
|
Appendix F |
|
|
Appendix G |
Extract of Meteorological Observations for Hong Kong Lau Fau Shan |
In accordance with the Updated Environmental Monitoring and Audit Manual (April 2022) for the Project, baseline environmental monitoring for air quality and water quality should be conducted prior to the commencement of construction works of the interim section of Road D1. Pursuant to EP Condition 3.3, Baseline Monitoring Report shall be submitted to the Director of Environmental Protection at least 2 weeks before the commencement of construction of the Project. As the construction works would commence by end of 2022, baseline monitoring for air quality and water quality were conducted according to the Updated Environmental Monitoring and Audit Manual (April 2022) before the commencement of construction works.
The baseline monitoring for 1-hour TSP monitoring was carried out between 9 December 2021 and 22 December 2021 at three air quality monitoring stations. Baseline 1-hour TSP monitoring was conducted at least three times per day at each monitoring station when the highest dust impact was expected. Data collected were reviewed and analyzed to establish the background air quality at three monitoring stations. Table A1 summarizes the results of the baseline 1-hour TSP monitoring.
Table A1 Summary of Baseline 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results
|
Stations |
Average (µg/m3) |
Range (µg/m3) |
Sampling Parameter |
|
AM23 |
62.1 |
51.0 71.0 |
1-hour TSP |
|
AM24 |
61.5 |
51.0 70.0 |
|
|
AM25a(1) |
77.2 |
62.0 98.0 |
NOTE:
(1) The air quality monitoring station AM25 is currently located at an open/ storage area that is deemed not suitable for setting up air quality monitoring station. An alternative monitoring station AM25a next to San Wai Sewage Treatment Plant is proposed and approved by the IEC and the EPD.
The baseline 1-hour TSP monitoring results form the basis for determining the air quality criteria for the impact monitoring. Table A2 presents the Action and Limit Levels for impact monitoring of 1-hour TSP.
Table A2 Calculated Action and Limit Levels for 1-hour TSP
|
Monitoring Stations |
Action Level (µg/m3) |
Limit Level (µg/m3) |
|
AM23 |
290.4 |
500 |
|
AM24 |
290.0 |
|
|
AM25a |
300.2 |
Baseline water quality monitoring was also carried out at six water quality monitoring stations. Data collected were reviewed and analyzed to establish the background water quality at these six monitoring stations. Table A3 summarizes the results of the baseline water quality monitoring.
Table A3 Summary of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Results
|
Locations |
Parameters |
|||||
|
Temperature (°C) |
pH |
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) (mg/L) (Middle) |
Turbidity (NTU) |
Suspended Solids (SS) (mg/L) |
||
|
U1 |
Avg. |
22.6 |
8.1 |
7.3 |
17.5 |
12.8 |
|
Min. |
19.9 |
7.3 |
4.3 |
4.7 |
3.7 |
|
|
Max. |
26.8 |
9.1 |
10.5 |
53.2 |
36.0 |
|
|
U2 |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.1 |
8.3 |
5.4 |
|
Min. |
20.3 |
7.3 |
3.4 |
2.5 |
1.3 |
|
|
Max. |
26.3 |
8.6 |
10.7 |
24.3 |
16.0 |
|
|
SW |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.2 |
11.5 |
6.2 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.4 |
3.5 |
1.9 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.4 |
8.6 |
10.7 |
23.2 |
24.0 |
|
|
HT |
Avg. |
22.6 |
8.0 |
6.9 |
16.2 |
15.4 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.3 |
2.2 |
2.8 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.1 |
8.7 |
10.6 |
45.1 |
69.0 |
|
|
TKW1 |
Avg. |
22.7 |
8.0 |
7.7 |
14.3 |
9.4 |
|
Min. |
20.3 |
7.4 |
2.8 |
3.4 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.4 |
8.7 |
10.8 |
63.2 |
54.0 |
|
|
TKW |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.0 |
14.4 |
10.2 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.4 |
2.4 |
4.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.3 |
8.7 |
10.3 |
57.3 |
52.0 |
|
The Action and Limit Levels for impact monitoring of water quality are presented in Table A4. They were derived based on the criteria specified in the Updated EM&A Manual.
Table A4 Derived Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality
|
Parameters |
Action Levels |
Limit Levels |
|
SW |
||
|
DO (mg/L) (3) |
3.7 |
3.5 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
21.4 |
22.9 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
9.7 |
9.9 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
HT |
||
|
DO (mg/L) (3) |
2.4 |
2.2 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
32.3 |
32.6 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
34.0 |
38.7 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
TKW1 |
||
|
DO (mg/L) (3) |
2.8 |
2.8 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
27.9 |
29.2 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
16.0 |
18.4 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
TKW |
||
|
DO (mg/L) (3) |
2.5 |
2.4 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
24.2 |
24.6 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
19.8 |
21.6 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
Notes:
(1) For DO, non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when monitoring result is lower than the limit.
(2) For Turbidity and Suspended Solids (SS), non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when monitoring result is higher than the limit.
(3) The derived Action Levels and Limit Levels for dissolved oxygen only apply to mid-depth.
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Background 1.1.1 The HSK/HT NDA occupies an area of approximately 714 ha and is located in the north-western part of the New Territories, midway between Tuen Mun and Tin Shui Wai New Towns. It is bounded by Tin Ying Road/ Ping Ha Road/ Kiu Hung Road to the east, Castle Peak Road to the south, Kong Sham Western Highway (KSWH) to the west, and Tin Ha Road, Lau Fau Shan Road and hillslopes along Deep Bay Road to the north. In the wider context, the proposed Project is strategically located in close proximity to Shenzhen, particularly Shenzhen Bay Control Point, Qianhai, and Shekou and efficiently linked with the Greater Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. The KSWH and the possible highway connecting the Project area with the Tuen Mun - Chek Lap Kok Link, the Hong Kong International Airport, Kwai Tsing Container Terminals, and the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge and its Boundary Crossing facilities. New strategic highway infrastructure connecting the Project area with the urban area will also be planned to address the long-term development needs of North West New Territories (NWNT). The proposed West Rail Hung Shui Kiu Station (HSK Station), with its alignment traversing the Project allows convenient and efficient access to and from the Project area. 1.1.2 The works under HSK/HT NDA Stage 1 works comprises the construction of interim section of new distributor road (Road D1) (hereinafter call the Project) that is a designated project (DP) (defined under item A1 in Schedule 2 of the Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance) connecting the site for the first batch of multi-storey buildings (MSBs) at Sites 3-6, 3-7 and 3-8 to the existing Ha Tsuen Roundabout of KSWH. 1.1.3 The HSK/HT NDA Stage 1 works would be implemented under a fast track programme, involving various complex tasks for providing infrastructure and forming the five development sites to be conducted in parallel, so as to tie in with operation of the development MSBs or other land-efficient means and population intake of the village resite house in 2025 tentatively. 1.1.4 The scope of works covered by Public Works Programme (PWP) Item No. 7796CL comprise the followings:
(i) Site formation works for Site 2-18, Site 2-19, Site 3-6, Site 3-7 and Site 3-8;
(ii) Land decontamination works including ground investigation works for Site 2-18, Site 2-19, Site 3-6, Site 3-7 and Site 3-8 and other areas within the boundaries of the site;
(iii) Construction of a district distributor road connecting to the existing interchange underneath KSWH, construction of local roads, widening of a section of Fung Kong Tsuen Road and associated junction/ road improvements; and
(iv) Engineering infrastructure works comprising sewerage works (including a pumping station), drainage works (including a detention pond), waterworks and landscaping works.
1.1.5 Acuity Sustainability Consulting Limited (ASCL) is commissioned by Civil Engineering and Development Department (CEDD) to undertake the Environmental Team (ET) services as required and/or implied, both explicitly and implicitly, in the Environmental Permit (EP), Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report (Register No. AEIAR-203/2016) and Environmental Monitoring and Audit (EM&A) Manual for the Project; and to carry out the EM&A programme in fulfillment of the EIA Reports, EM&A requirements under Service Contract No. WD/02/2021. 1.1.6 Pursuant to the Environmental Impact Assessment Ordinance (EIAO), the Director of Environmental Protection Department (EPD) granted the Environmental Permits (Nos.: EP-526/2017, EP-527/2017, EP-528/2017, EP-529/2017, EP-530/2017 and EP-531/2017) to the CEDD for the Project. The HSK/HT NDA Stage 1 works comprise the interim section of Road D1 that is governed under Environmental Permit No. EP-528/2017. No other DPs are identified within the scope of HSK/HT NDA Stage 1 works. 1.2 Purpose of the Report 1.2.1 According to Appendix A of the Updated EM&A Manual for the Project, baseline monitoring for air quality and water quality should be conducted prior to the commencement of construction works. No designated noise monitoring stations are located with the 300 m buffer zone of the interim section of Road D1. As such, baseline (and construction phase) noise monitoring for Road D1 (interim section) is not recommended. 1.2.2 The EM&A requirements for baseline monitoring under Contract No. YL/2020/03 are set out in the Updated EM&A Manual (April 2022) and Contract Specification. Environmental aspect of air quality and water quality were identified as the key issues requiring implementation of monitoring programme during the construction phase of the Project. 1.2.3 This report presents the monitoring methodology, findings and results for the baseline air quality and water quality monitoring of the Project. According to the Updated EM&A Manual (April 2022), baseline landscape and visual monitoring should also be conducted. The results are reported in a separate standalone Baseline Landscape and Visual Monitoring Report. 1.3 Report Structure 1.3.1 This Baseline Monitoring Report comprises the following sections:Section 1 introduces the background of the Project and purpose of this Report;
Section 2 presents the baseline monitoring methodologies, requirements, results, influencing factors, as well as determination of the action and limit levels of air quality;
Section 3 presents the baseline monitoring methodologies, requirements, results, influencing factors, as well as determination of the action and limit levels of water quality; and
Section 4 concludes the findings of baseline monitoring.
2 AIR QUALITY 2.1 Monitoring Requirement 2.1.1 Baseline air quality monitoring shall be carried out to determine the ambient 1-hour Total Suspended Particulates (TSP) levels at designated monitoring stations for 14 consecutive days prior to the commissioning of the construction works. 1-hour TSP monitoring should be carried out at least three times per day at each monitoring station when the highest dust impact are expected. 2.2 Monitoring Equipment and Methodology 2.2.1 Direct reading dust meters were used for measuring 1-hour TSP levels during the baseline air quality monitoring. According to paragraph 4.3.5 of the Updated EM&A Manual, the proposed use of direct reading dust meter was submitted to and agreed by the IEC. 2.2.2 The direct reading dust meters have been calibrated against high volume samples (HVSs) annually. A 2-day, three 3-hour measurement results per day from direct reading dust meters were taken to compare with the sampling results from the HVSs. The correlation between the direct reading dust meters and the HVSs were then concluded. By accounting for the correlation factor, the direct reading dust meters are considered to achieve comparable results as that of the HVSs. 2.2.3 Sufficient number of monitoring instruments were prepared by the ET for carrying out the baseline monitoring. All equipment and associated instrumentation were clearly labelled. 2.2.4 Equipment used in the baseline air quality monitoring programme is summarized in Table 2.1. Calibration certificates for the air quality monitoring equipment are attached in Appendix A.Table 2.1 Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Serial No. |
|
Direct Reading Dust Meter |
Aerocet 831 |
A14259 |
|
Sibata LD-5R |
851816 |
|
|
851820 |
||
|
992818 |
Table 2.2 Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Parameters, Frequency and Duration
|
Parameters |
Duration |
Frequency |
|
1-hour TSP |
Daily for at least 14 consecutive days |
3 times per day |
Table 2.3 Original Air Quality Monitoring Stations for Baseline and Impact Monitoring
|
Station(s) |
EIA ID |
Monitoring Location |
|
AM23 |
P1032 |
Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-6) |
|
AM24 |
P1501 |
Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-8) |
|
AM25 |
P606 |
Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-14) |
(i) At location close to the major dust emission source;
(ii) Close to the (planned) air sensitive receivers as defined in the EIAO-TM;
(iii) Proper position/ sitting and orientation of the monitoring equipment; and
(iv) Take into account the prevailing meteorological conditions (the prevailing meteorological conditions at AM25 and AM25a will be very similar as they are located at a flat land without barriers and around 100 m away from each other).
2.4.3 The Proposal for Alternative Monitoring Station (Air Quality) for monitoring station AM25a has been verified by the IEC and endorsed by the EPD. The updated locations for air quality monitoring are listed in Table 2.4.Table 2.4 Updated Air Quality Monitoring Stations for Baseline and Impact Monitoring
|
Station(s) |
EIA ID |
Monitoring Location |
|
AM23 |
P1032 |
Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-6) |
|
AM24 |
P1501 |
Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-8) |
|
AM25a |
- |
San Wai Sewage Treatment Plant near the Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-14) |
Table 2.5 Photos of Baseline Air Quality Monitoring Stations
|
ID |
Direct reading dust meter Position |
Monitoring direction |
|
AM23 |
|
|
|
AM24 |
|
|
|
AM25a |
|
|
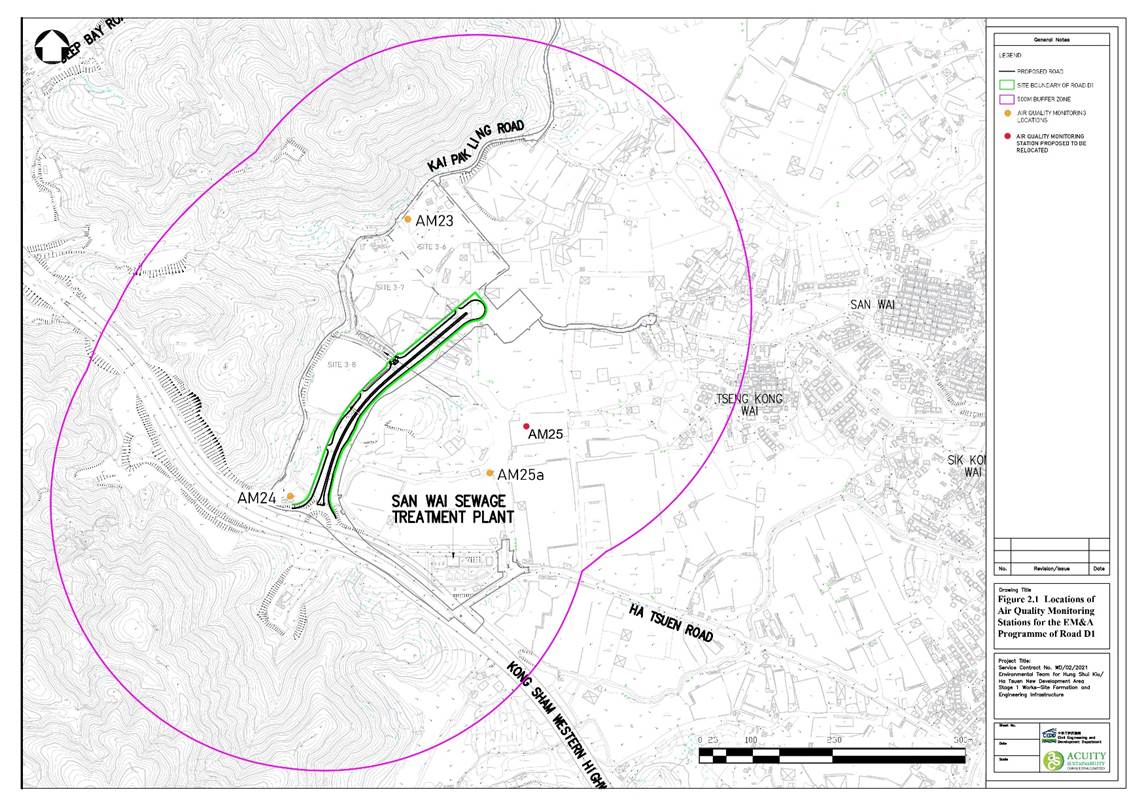
Figure 2.1 Air Quality Monitoring Locations
2.5 Results and Observations 2.5.1 Baseline monitoring for air quality was conducted from 9 December 2021 to 22 December 2021 (Figure 2.2). The baseline air quality monitoring result are summarized in Table 2.6. Details of air quality results are presented in Appendix B. 2.5.2 During the baseline monitoring, no construction activity of the Project was conducted in the vicinity of the monitoring locations and in the project site. 2.5.3 No other major dust emission sources were noted. Weather condition of the whole baseline monitoring period was sunny and fine. Extracts of Meteorological Observations for Hong Kong available from the Hong Kong Observatory Lau Fau Shan, which reflect the weather summary of the baseline air quality monitoring period, are presented in Appendix G.
Table 2.6 Summary of Baseline 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results
|
Monitoring Station (s) |
TSP Concentration, μg/m3 |
||
|
Average |
Min. |
Max. |
|
|
AM23 - Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-6) |
62.1 |
51.0 |
71.0 |
|
AM24 - Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-8) |
61.5 |
51.0 |
70.0 |
|
AM25a - San Wai Sewage Treatment Plant near the Planned Port Back-up, Storage and Workshop (at Site 3-14) |
77.2 |
62.0 |
98.0 |
Table 2.7 Action and Limit Levels for Air Quality during Construction Period
|
Parameters |
Action Level (µg/m3) |
Limit Level (µg/m3) |
|
1-hour TSP Level (µg/m3) |
BL ≤ 384 µg/m3, AL = (BL × 1.3 + LL)/2 BL > 384 µg/m3, AL = LL |
500 |
Table 2.8 Calculated Action and Limit Levels for 1-hour TSP
|
Monitoring Station(s) |
Action Level (µg/m3) |
Limit Level (µg/m3) |
|
AM23 |
290.4 |
500 |
|
AM24 |
290.0 |
|
|
AM25a |
300.2 |
Table 3.1 Parameters measured in the Baseline Water Quality Monitoring
|
Parameters |
Units |
Abbreviations |
Frequency |
|
In-situ measurements |
3 days per week for at least 4 weeks (the interval between 2 sets of monitoring should not be less than 36 hours) |
||
|
Dissolved oxygen |
mg/L |
DO |
|
|
Dissolved oxygen saturation |
% |
DO% |
|
|
Temperature |
oC |
- |
|
|
pH |
- |
- |
|
|
Turbidity |
NTU |
- |
|
|
Laboratory measurements |
|||
|
Suspended Solids |
mg/L |
SS |
|
Table 3.2 Original Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Station |
Description |
Easting |
Northing |
|
U1 |
Upstream Station |
815936 |
834150 |
|
U2 |
Upstream Station |
816240 |
834009 |
|
SW |
Gradient station (downstream of U1 and the construction site of Road D1) |
816304 |
834321 |
|
HT |
Gradient station (downstream of U2 and the construction site of Road D1) |
816866 |
834314 |
|
DB |
Gradient station |
816091 |
834976 |
Table 3.3 Updated Locations of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Station |
Description |
Easting |
Northing |
|
U1 |
Upstream Station |
815936 |
834150 |
|
U2 |
Upstream Station |
816240 |
834009 |
|
SW |
Gradient station (downstream of U1 and the construction site of Road D1) |
816304 |
834321 |
|
HT |
Gradient station (downstream of U2 and the construction site of Road D1) |
816866 |
834314 |
|
TKW1 |
Gradient station (downstream of the construction site of Road D1) |
816563 |
834686 |
|
TKW |
Gradient station (downstream of TKW1 and construction site of Road D1) |
816594 |
834690 |
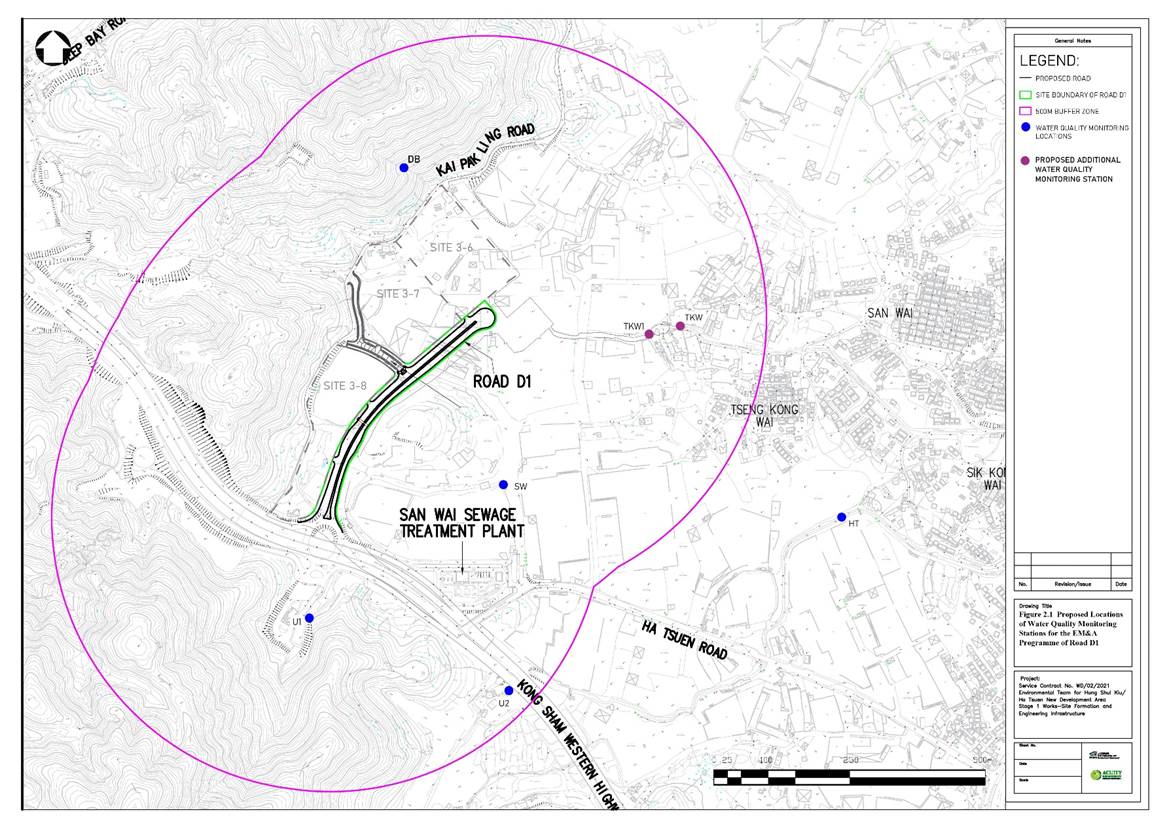
Figure 3.1 Locations of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Stations
3.4 Monitoring Equipment and Methodology 3.4.1 In-situ measurements at monitoring locations including DO, DO%, pH, temperature and turbidity were collected using the equipment listed in Table 3.4 and the detection limit for the in-situ measurement are shown in Table 3.5. Calibration certificates for the water quality monitoring equipment are attached in Appendix A. 3.4.2 Water samples for suspended solids (SS) analysis were stored in high density polythene bottles, packed in ice (cooled to 4 ºC without being frozen), and delivered to a HOKLAS laboratory as soon as possible after collection of the water samples.
Table 3.4 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Quantity |
|
Water Sampler |
Kahlsico Water Sampler 13SWB20 |
1 |
|
Multi Parameter Water Quality System |
HORIBA U-53 |
2 |
Table 3.5 Detection Limits and Precision for Water Quality Determinates
|
Parameters |
Detection limit |
Accuracy |
Precision |
|
DO |
0 20 mg/L |
± 0.1 mg/L |
25% |
|
Temperature |
0 45 oC |
± 0.1 oC |
|
|
pH |
0 14 |
± 0.1 |
|
|
Turbidity |
0 1000 NTU |
± 2 |
3.4.3 During the baseline monitoring, the depths of waters at the monitoring stations were all less than 3 m. Thus, only mid-depth samples were collected. For in situ measurements, duplicate readings were made at each station. Duplicate water samples were also collected at each station. 3.4.4 In-situ monitoring instruments for water quality parameters were checked, calibrated and certified by a laboratory accredited under HOKLAS before use. Responses of sensors and electrodes were checked with certified standard solutions before each use. Wet bulb calibration for a DO meter was carried out before measurement at each monitoring day. 3.5 Laboratory Measurement and Analysis 3.5.1 Analysis of SS was carried out in a HOKLAS accredited laboratory, Acumen Laboratory and Testing Limited (Reg. No. HOKLAS 241). Sufficient water samples were collected at each of the monitoring stations for carrying out the laboratory SS determination. 3.5.2 The SS determination works started within 24 hours after collection of the water samples. The analysis followed the APHA 2540D analytical method with the detection limit of 1.0 mg/L. The quality assurance and quality control results are presented in Appendix D. The HOKLAS Laboratory Certificate is attached in Appendix F.
3.5.3 Parameters for laboratory measurements, their standard methods and the detection limits are presented in Table 3.6.
Table 3.6 Analytical Methods Applied to Water Quality Samples
|
Parameter |
Standard Method |
Detection Limit |
Accuracy |
|
Suspended Solids (mg/L) |
APHA 2540D |
1.0 mg/L |
±17% |
Table 3.7 Summary of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Results
|
Locations |
Parameters |
|||||
|
Temperature (°C) |
pH |
DO (mg/L) (Middle) |
Turbidity (NTU) |
SS (mg/L) |
||
|
U1 |
Avg. |
22.6 |
8.1 |
7.3 |
17.5 |
12.8 |
|
Min. |
19.9 |
7.3 |
4.3 |
4.7 |
3.7 |
|
|
Max. |
26.8 |
9.1 |
10.5 |
53.2 |
36.0 |
|
|
U2 |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.1 |
8.3 |
5.4 |
|
Min. |
20.3 |
7.3 |
3.4 |
2.5 |
1.3 |
|
|
Max. |
26.3 |
8.6 |
10.7 |
24.3 |
16.0 |
|
|
SW |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.2 |
11.5 |
6.2 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.4 |
3.5 |
1.9 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.4 |
8.6 |
10.7 |
23.2 |
24.0 |
|
|
HT |
Avg. |
22.6 |
8.0 |
6.9 |
16.2 |
15.4 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.3 |
2.2 |
2.8 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.1 |
8.7 |
10.6 |
45.1 |
69.0 |
|
|
TKW1 |
Avg. |
22.7 |
8.0 |
7.7 |
14.3 |
9.4 |
|
Min. |
20.3 |
7.4 |
2.8 |
3.4 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.4 |
8.7 |
10.8 |
63.2 |
54.0 |
|
|
TKW |
Avg. |
22.7 |
7.9 |
7.0 |
14.4 |
10.2 |
|
Min. |
20.2 |
7.4 |
2.4 |
4.0 |
<1.0 |
|
|
Max. |
26.3 |
8.7 |
10.3 |
57.3 |
52.0 |
|
Figure 3.2 Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Schedule
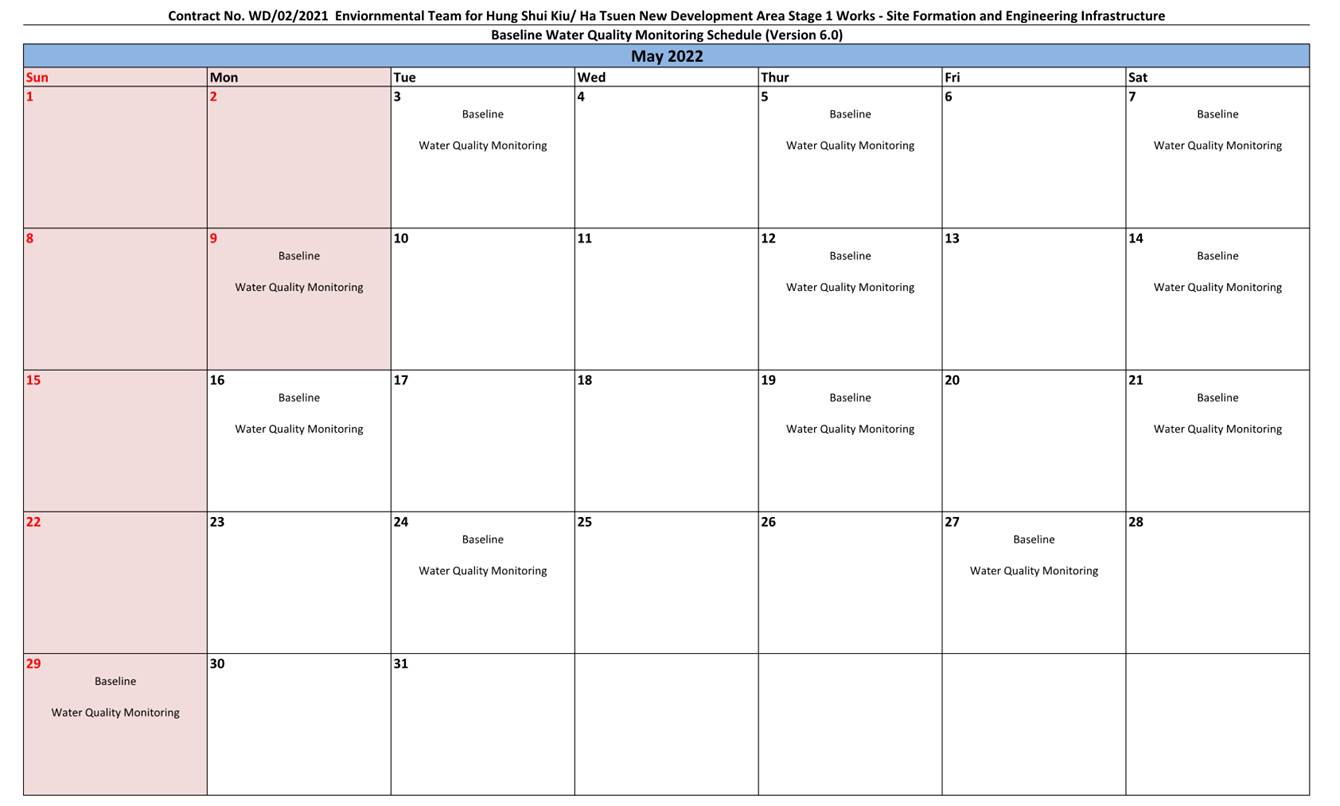
Table 3.8 Determination of Action and Limit Levels of Water Quality for Impact Monitoring
|
Parameters |
Action |
Limit |
|
DO in mg/L |
Surface and Middle, Bottom DO ≤5%-ile of baseline data |
Surface and Middle DO ≤4 mg/L and 1%-ile of baseline data for surface and middle layers Bottom DO ≤2 mg/L and 1%-ile of baseline data for bottom layer |
|
SS in mg/L |
Depth-averaged SS · ≥ 95%-ile of baseline data or · 120% of upstream control station of the same day (applicable to station at SW and HT only) |
Depth-averaged SS · ≥ 99%-ile of baseline data or · 130% of upstream control station of the same day (applicable to station at SW and HT only) |
|
Turbidity in NTU |
Depth-averaged Turbidity · ≥ 95%-ile of baseline data or · 120% of upstream control station of the same day (applicable to station at SW and HT only) |
Depth-averaged Turbidity · ≥ 99%-ile of baseline data or · 130% of upstream control station of the same day (applicable to station at SW and HT only |
|
pH |
Beyond the range 6.6 8.4 |
Beyond the range of 6.5 8.5 |
(1) For DO, non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when monitoring result is lower than the limit.
(2) For
SS and turbidity, non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when
monitoring result is higher than the limit.
Table 3.9 Derived Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality
|
Parameters |
Action Levels |
Limit Levels |
|
SW |
||
|
DO (mg/L) |
3.7 |
3.5 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
21.4 |
22.9 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
9.7 |
9.9 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
HT |
||
|
DO (mg/L) |
2.4 |
2.2 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
32.3 |
32.6 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
34.0 |
38.7 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
TKW1 |
||
|
DO (mg/L) |
2.8 |
2.8 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
27.9 |
29.2 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
16.0 |
18.4 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
|
TKW |
||
|
DO (mg/L) |
2.5 |
2.4 |
|
Turbidity (NTU) |
24.2 |
24.6 |
|
SS (mg/L) |
19.8 |
21.6 |
|
pH |
Less than 6.6 or greater than 8.4 |
Less than 6.5 or greater than 8.5 |
Notes:
(1) For DO, non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when monitoring result is lower than the limit.
(2) For Turbidity and SS, non-compliance of the water quality limit occurs when monitoring result is higher than the limit.
(3) The derived Action Levels and Limit Levels for dissolved oxygen only apply to mid-depth.
4 COMMENTS AND CONCLUSION 4.1 Revision for Inclusion in the EM&A Manual 4.1.1 The baseline monitoring was conducted according to the Updated EM&A Manual for air quality and water quality. 4.1.2 All updated air quality and water quality monitoring locations were verified by the IEC and approved by the EPD. 4.1.3 The monitoring methodology, parameters monitored, and monitoring locations are all generally in line with the Updated EM&A Manual for the Project. 4.2 Air Quality 4.2.1 Baseline air quality monitoring was carried out between 9 December 2021 and 22 December 2021 at three monitoring stations. 4.2.2 No construction activity of the Project was conducted in the vicinity of the monitoring locations and in the project site. 4.2.3 Action and Limit Levels were derived from the baseline 1-hour TSP monitoring results according to the Updated EM&A Manual. 4.3 Water Quality 4.3.1 Baseline water quality monitoring was conducted between 3 May 2022 to 29 May 2022 at six monitoring stations (i.e. U1, U2, SW, HT, TKW1 and TKW). 4.3.2 Action and Limit Levels were derived from the baseline water quality monitoring results according to the Updated EM&A Manual. 4.4 Comments/ Recommendations 4.4.1 The baseline water quality monitoring was conducted during a typical wet season in Hong Kong. During the dry season, however, the rainfall is less, and the stream flow would contain higher portion of expedient discharge from local village houses and contaminated runoff from brownfield sites/ open storage area. It is anticipated that the stream flow would contain higher content of turbidity and SS during the dry season. Thus, review of the water quality baseline condition would be required during the construction phase of the Project, particularly when the non-project related exceedances of Action and Limit Levels become frequent. The environmental performance criteria may need to be updated if it is evident that the baseline conditions have changed significantly. If feasible, a supplementary baseline EM&A programme would be carried out to collect the latest background water quality data for review and updating of the environmental performance criteria.